Maps
A Map is a data type which consists of a set of distinct keys that each map to a specific value.

A Map is also known as a Dictionary, since it can be used to store items in a similar manner as a dictionary, where each word maps to a specific definition. These are the basic methods of a Map:
put(key, value)- Adds the key and value to the map, so they are now associated with each other. If this key was already in the Map, it will now point to the new value only.get(key)- Returns the value that the key maps to.remove(key)- Removes the key-value mapping of this key from the map.containsKey(key)- This returns true if the key is in the map and false otherwise (like thecontainsmethod of Set).
Maps vs. Lists
In a List (or Array), every item is stored at a specific index from 0 to N, the size of the List. Each item can be accessed by specifying the integer it is stored at.
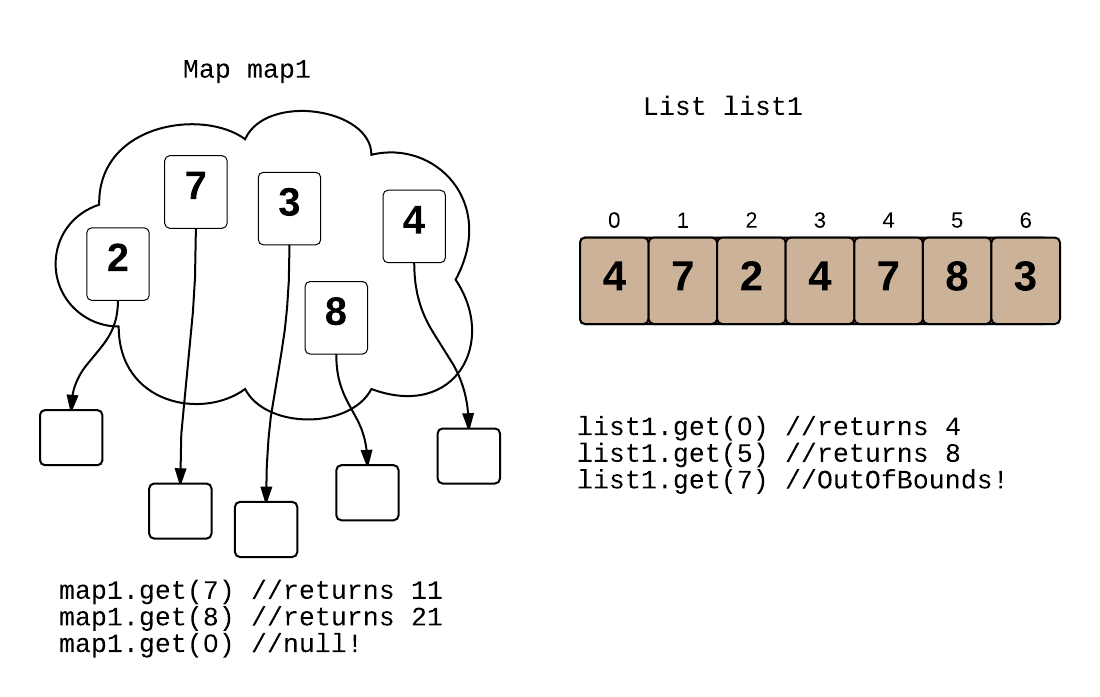
A Map's keys are similar to a List's indices, but the keys are specified to any values, while indices are just in order from 0 to the size of the list. Lists are used for ordering elements while maps are for mapping keys to values.
Map Classes
Java provides the interface Map which defines the standard Map methods, and the HashMap is the commonly used Map Class. See the Learneroo HashMap reference to learn more.
See Ruby Hashes, Python Dictionaries, Javascript Objects to learn about the Map equivalents in those languages.
Using a Map
Maps are useful in many cases, such as when you want to track information about a set of elements. Use a Map to solve the following challenge in an optimal manner.
Challenge
Find the number in each list of numbers that appears the most times.
For example, in the list {1, 1, 2, 3, 2, 2}, print 2, since it appears 3 times, more than any other number.
(Unlike Duplicate Duplicates, these numbers can be anywhere within the range of Java integers.)
Challenge
Print the number in each list that appears the most times.
Please sign in or sign up to submit answers.
Alternatively, you can try out Learneroo before signing up.