Rails Model Reference
See Rails Model and Data for our guide through this topic.
Terminal Commands
rails new store- Create a new Rails app from scratch in a new store folder.
The following commands are entered in the terminal in your app's directory:
bundle install- Install the gems (bundled Ruby libraries) for your Rails App.rails generate model Product name:string- Create Product model with a columnname(which will store strings of text).rails g migration AddPriceToProducts price:integer- generates the migration file to add an integer price column to the product table.rake db:migrate- Run migration files to apply changes to your database.rake test- Run your application's tests.
Rails Console
You can connect with your app/database and perform standard CRUD operations in the Rails console. This is useful for trying code out.
rails console(orrails c) - Enter this command in your terminal to start the Rails console.reload!- Enter this in your running Rails console to reload changes
(See Active Record Migrations and the Rails Command Line for more.)
CRUD
These are the 4 basic "CRUD" operations:
- Create -
Product .create(name: "Phonograph" , description: "Records sound" )- Creates and saves a new record to the database. Use.newto instantiate an object without saving it until.saveis called. - Read - There are many methods for reading data, such as:
products = Product .all- return collection of all productsproducts = Product .where(name: "Hammer" , price: 10)- returns all products with both these attributesproduct = Product .find_by(name: "Cow" )- returns first product named "Cow"
- Update - After retrieving a record, you can modify and save it:
product.description = "It moos"
product.save - Delete - Don't like your Cow? You can remove it from the database:
product.destroy
See Active Record Basics and Active Record Query Interface for more.
Model Relationships
Add a column_id to products to associate each product with a category:
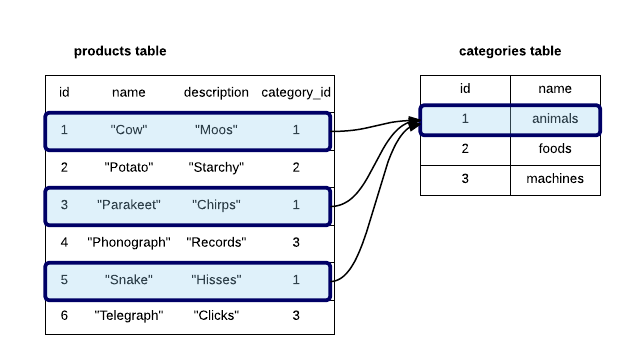
Associate products with a category in Rails:
class Product < ActiveRecord::Base
belongs_to :category
end
Associate categories with many products:
class Category < ActiveRecord::Base
has_many :products
end
You can now use this code:
cat1 = Category.first
cat1.products #returns products in `cat1`
prod1 = Product.first
prod1.categories # returns category of `prod1`
See Active Record Associations for more.
Validations
Validations are added to a model to ensure only valid data is saved to the database. Here's the format for a simple validation:
validates :column, property: value
For example:
validates :name, presence: true
This will ensure that records have a name before they are saved to the database.
See Rails Validations for more.